What Are the Latest Advancements in Sexual Health Treatments?

Sexual health plays a crucial role in overall well-being, and researchers continue to explore new treatments to help individuals struggling with sexual dysfunctions. Exciting advancements in medical technology offer promising solutions, including low-intensity shockwave therapy (LiSWT), stem cell therapy, and platelet-rich plasma (PRP) therapy. While these treatments show potential, they also have limitations that need to be addressed through further research.
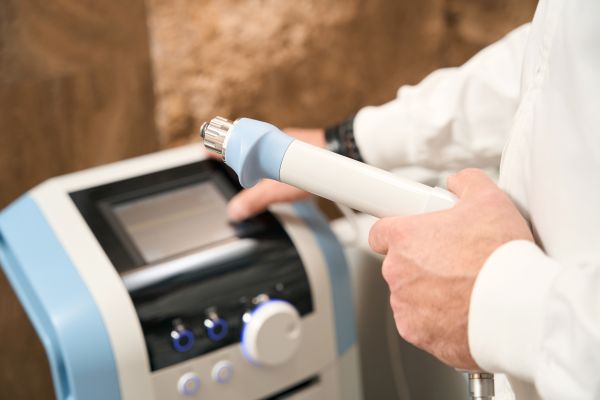
Low-Intensity Shockwave Therapy (LiSWT)
LiSWT is a non-invasive treatment that uses sound waves to improve blood flow to the genitals. Originally developed for kidney stones and musculoskeletal injuries, researchers found that LiSWT could also enhance erectile function by stimulating blood vessel growth. This treatment is primarily being investigated for erectile dysfunction (ED) and Peyronie’s disease, a condition that causes curvature of the penis.
Potential Benefits:
- Increases blood circulation and encourages new blood vessel formation.
- Can be an alternative to medications like Viagra for men who do not respond well to them.
- Non-invasive, meaning no surgery or injections are required.
Current Limitations:
- LiSWT is still not FDA-approved for ED, as more studies are needed to confirm long-term effectiveness.
- Treatment protocols vary, making it unclear how many sessions are needed for optimal results.
- It may not work for individuals with severe vascular damage or advanced ED.
Stem Cell Therapy
Stem cell therapy is an innovative approach that aims to regenerate damaged tissues using the body’s own healing mechanisms. In sexual health, it is being studied primarily for erectile dysfunction and vaginal atrophy (reduced elasticity and thinning of vaginal tissues, often linked to menopause). Stem cells, usually derived from bone marrow or fat tissue, can potentially repair damaged blood vessels and nerve endings, improving function.
Potential Benefits:
- Could provide long-lasting results by regenerating tissue rather than just treating symptoms.
- May help individuals who have not responded to conventional therapies.
- Research is expanding to explore its use for female sexual dysfunction.
Current Limitations:
- Still in experimental stages; not widely available for clinical use.
- Ethical and regulatory concerns over the use of stem cells.
- Studies are mostly small-scale, requiring larger trials to prove effectiveness and safety.
Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy
PRP therapy involves drawing a small amount of a patient’s blood, processing it to concentrate the platelets, and injecting it into targeted areas to promote healing. In sexual health, PRP has been explored as a treatment for erectile dysfunction, vaginal rejuvenation, and even conditions like lichen sclerosus, a chronic inflammatory skin disorder affecting the genital area.
Potential Benefits:
- Uses the body’s own healing properties to regenerate tissues.
- Could improve sensitivity, arousal, and sexual function in both men and women.
- Minimally invasive and has fewer side effects compared to surgical treatments.
Current Limitations:
- Research is still in early stages, and results vary between individuals.
- The procedure is not standardized, leading to inconsistencies in effectiveness.
- It is often costly and not covered by insurance.
The Future of Sexual Health Treatments
While these advancements offer new hope, it is essential to approach them with realistic expectations. Many of these treatments are still undergoing research, and their long-term benefits and risks remain unclear. If you are considering any of these therapies, consult with a medical professional to determine the best approach based on your specific needs and health conditions.
By staying informed about the latest research and advancements, individuals struggling with sexual health issues can explore new options while maintaining realistic expectations about their effectiveness and availability.
References:
- Albersen, M., Weyne, E., & Bivalacqua, T. J. (2013). Stem cell therapy for erectile dysfunction: progress and future directions. Sexual Medicine Reviews, 1(1), 50-64. https://doi.org/10.1002/smrj.5
- Clavijo, R. I., Kohn, T. P., Kohn, J. R., & Ramasamy, R. (2017). Effects of low-intensity extracorporeal shockwave therapy on erectile dysfunction: a systematic review and meta-analysis. The journal of sexual medicine, 14(1), 27-35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsxm.2016.11.001
- Dankova, I., Pyrgidis, N., Tishukov, M., Georgiadou, E., Nigdelis, M. P., Solomayer, E.-F., Marcon, J., Stief, C. G., & Hatzichristou, D. (2023). Efficacy and safety of platelet-rich plasma injections for the treatment of female sexual dysfunction and stress urinary incontinence: A systematic review. Biomedicines, 11(11), 2919. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11112919
- Vardi, Y., Appel, B., Kilchevsky, A., & Gruenwald, I. (2012). Does low intensity extracorporeal shock wave therapy have a physiological effect on erectile function? Short-term results of a randomized, double-blind, sham controlled study. Journal of Urology, 187(5), 1769-1775. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.juro.2011.12.117